XMLMC API Quickstart
Home > Integration > XMLMC API Quickstart Guide
Related Articles |
Communication
One needs to POST a payload to a https endpoint with the HTTP headers containing the Authorisation. One can read up on other technical considerations in the FAQ:Hornbill API's & Webhooks.
Transmission
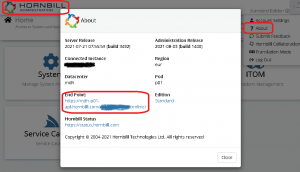
Data is to be sent over https (port: 443) to a given endpoint. The endpoint is different for each method you call. One can find the endpoint BASE URL for your particular instance by either viewing the About-section in Hornbill Administration or by looking at the response of https://files.hornbill.com/instances/<instance_name>/zoneinfo
The endpoint for the methods will then be followed by "xmlmc" before the "service" and the "method" within that service. This in turn is followed by a query string referencing the method. e.g. BASE URL / xmlmc / service?op=method
Documentation
The endpoint base obtained, with the addition of "xmlmc/", will lead to the documentation on what methods are available (https://api.hornbill.com/xmlmc/ API).
The main page is grouped into two sections: Services and Applications.
Services are overall methods that the platform provides, whereas Applications define the functionality particular to the listed Applications. For instance: sending an email is a platform method and logging a request if particular to Service Manager.
Service
Within Hornbill there are various overall
Application
Each application, which you have installed on your instance (including core), will be listed here. Within each Application, you will find two lists: Entities and Operations (at the bottom). These are the actions that are specific to the particular application.
Each Entity might also have "Operations" associated to them. From a programming perspective, an Entity is effecively an Object type behind the scenes. The Operations associated to these entities are effectively functions operating on entities of the given type (eg creation, changing status etc).
As of this writing, in com.hornbill.core, the first entity::operation combination is Achievement::addAchievement. The first Operation listed is addEveryoneToRole.
The endpoint for Achievement::addAchievement is https://api.hornbill.com/INSTANCE/xmlmc/apps/com.hornbill.core/Achievement?op=addAchievement
The endpoint for addEveryoneToRole is https://api.hornbill.com/INSTANCE/xmlmc/apps/com.hornbill.core/?op=addEveryoneToRole
Authorisation
The HTTP-header will need to contain the API Key which must be generated in the user's profile within the Hornbill Administration.
We will be using the Authorization -header with ESP-APIKEY prefixing the API key which can be obtained from the Hornbill Administration (API Keys).
- The API key generated, belongs to the account under which it was generated. It takes on the permissions of that account. IF the account is not allowed to do something (via the GUI; eg access a particular call), then the API key will not be able to access that call either.
The default payload is expected to be XMLMC, so we will set the Content-Type-header accordingly.
Content-Type: text/xmlmc Authorization: ESP-APIKEY ###32 hexadecimal characters####
The default response payload will be of in XML (text/xmlmc).
- It is important to note that, when using XMLMC, the parameters must be passed to the operation in the same order as they appear in their definitions in order to satisfy the requirement of the input validation checks.
JSON
It is also possible to handle both payloads in JSON. In order to be able to send JSON, one needs to set the Content-Type-header to application/json. By setting the Accept-header to application/json the response will be in JSON.
- The JSON response payload will contain an @ sign as the first character in a property name. Not all JSON decoders will accept this.
Samples
XMLMC Sample
XML Payload to add an entry to the Timeline of a Request (please note that both the request must exist as well as the account (of which the API Key is used) must be able to see the Request (i.e. via Service visibility etc) else errors will occur).
Content-Type: text/xmlmc Authorization: ESP-APIKEY ... <methodCall service="apps/com.hornbill.servicemanager/Requests" method="updateReqTimeline"> <params> <requestId>IN00001234</requestId> <content>Hello Service Manager XMLMC World</content> <visibility>trustedGuest</visibility> </params> </methodCall>
Resulting payload:
<methodCallResult status="ok">
<params>
<activityId>urn:buzz:activity:...</activityId>
<flowCodeDebugState>
<executionId>...</executionId>
</flowCodeDebugState>
</params>
</methodCallResult>
The flowCodeDebugState-structure can be ignored - it is useful for debugging in the log files.
JSON Sample
The JSON below is the SAME as the XML Request payload given above.
Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: ESP-APIKEY ...
Accept: application/json
{
"methodCall": {
"@service": "apps/com.hornbill.servicemanager/Requests",
"@method": "updateReqTimeline",
"params": {
"requestId": "IN00001234",
"entity":"Hello Service Manager JSON World",
"visibility": "trustedGuest"
}
}
}
Resulting payload:
{
"@status": true,
"params": {
"activityId": "urn:buzz:activity:..."
},
"flowCodeDebugState": {
"executionId": "d385d755-7468-4d6b-9629-b0891c59fc1c"
}
}