Difference between revisions of "Package Creator"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{bluebanner|[[Main_Page|Home]] > [[Administration]] > [[IT Operations Management|ITOM]] > Package Creator|[[:Category:ITOM|Index]]}} | {{bluebanner|[[Main_Page|Home]] > [[Administration]] > [[IT Operations Management|ITOM]] > Package Creator|[[:Category:ITOM|Index]]}} | ||
{{IntroAndLinks | {{IntroAndLinks | ||
| − | |The | + | | |
| − | + | The Package Creator allows a user, with the necessary programming background and ability, to create Operations within Packages. A Package consists of a single Package Info file and with additional resource files where required. The info file contains all the details regarding operations and all parameters that may be necessary. Although it is possible to manually create a Package, a form-based editor is provided to simplify the process. An interface is also provided to facilitate the uploading and organisation of resources that may be required to facilitate operations. These resources may be scripts, executables or other required files. In addition to uploading scripts, an interface is also provided to allow for various file types to be created via the browser interface. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
* [[ITOM Package Library]] | * [[ITOM Package Library]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | ==Package Creator List== | ||
| + | [[File:PackageCreatorListFade.png|right|350px|link=https://wiki.hornbill.com/images/6/6e/PackageCreatorList.png]] | ||
| + | :{| | ||
| + | |- valign="top" | ||
| + | |style="width:500px"| | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Package|Unique name given to the Package}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Purpose|Summary of the intended use of the package}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Target OS|Operating System that the package was designed for execution}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Published|Late Published version of the packacge}} | ||
| + | |style="width:500px"| | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Created On|Date that the package was created}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Created By|The account used to create the package}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Last Updated On|Date the package was last updated}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Last Updated By|The account last used to update the package}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Toolbar=== | ||
| + | :{| | ||
| + | |- valign="top" | ||
| + | |style="width:500px"| | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Refresh|}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Target OS|}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet2|All|}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet2|Unknown|}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet2|Windows 32-bit|}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet2|Windows 64-bit|}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet2|Windows Universal|}} | ||
| + | |style="width:500px| | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Purpose|Dynamic list populated from the Purpose field of entriies in the list}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Filter|Free text filter on Package}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|[[#Create a Package|Cereate a Package]]|Create an IT Automation Package}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Delete|Delete selected Package(s)}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Create a Package== | ||
| + | Select the [+] button from the toolbar and when requested, enter a unique Package name. This will display Package Details where the package can be Configured and Updated via the Package Content Frame and Properties Form. | ||
| + | ===Package Content Toolbar=== | ||
| + | [[File:PackageContentEmptyFrame.png|right|350px]] | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Upload|Uploads files to the current folder}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|New Folder|Creates a new Folder}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|New File|Creates a new file in the current folder}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Baseline|Creates a new baseline of the current package}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Save|Saves amended package details}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Selecting '''Package Info''' file enables the file to be modified via a form or in its native XML format, which is selectable via the toggle buttons. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-collapsetext="Show Less" data-expandtext="Form View" style="width:100px"> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content" style="width:1000px"> | ||
| + | [[File:PackagePropertiesFormFade.png|350px|right|link=https://wiki.hornbill.com/images/5/5d/PackagePropertiesForm.png]] | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Package ID|A GUID which uniquely identifies the package) will be generated on creation}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Package|}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Description|Description of the packages content}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Purpose|Summary of the intended use of the package}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Vendor ID|Defined by the creator of the package (Hornbill packages will set to "private:hornbill")}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Target OS|Defines Target OS platform that the package is designed}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet2|Windows 32-bit|}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet2|Windows 64-bit|}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet2|Windows Universal|Package can be invoked on either Windows 32 or 64-bit}} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-collapsetext="Show Less" data-expandtext="XML View" style="width:100px"> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content" style="width:1000px"> | ||
| + | [[File:PackagePropertiesXml.png|link=https://wiki.hornbill.com/images/9/93/PackagePropertiesXml.png]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | ====Package Operations==== | ||
| + | [[File:PackageOperationsFormFade.png|right|]] | ||
| + | Operations various actions to be configured, which execute a single command, executable, script or installer package. An Operation is created by clicking on the Add Operation button within the Form View. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Bullet1|Operation|Mandatory Name used to select the package when creating a Job}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Description|Describes the functionality provided by the operation}} | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-collapsetext="Show Less" data-expandtext="Read More" style="width:500px"> | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Command Type|Provides a list of supported command types}} | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | {{Bullet2|Run Command|Executes a standalone command}} | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-collapsetext="Show Less" data-expandtext="Read More" style="width:500px"> | ||
| + | {{Bullet2|Windows Installer|Executes an uploaded Windows Installer(.msi) package, with one of four actions are available}} | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | {{Bullet3|Install Software|Installs the .msi package}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet3|Run Program|Executes the Installed program}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet3|Uninstall Software|Uninstall an .msi package}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet3|Update Software|Update an Installed .msi package}} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | {{Bullet2|Windows Executable|Executes a windows executable, selected from the Run File list}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet2|Batch Script|Excutes a Windows batch script (.cmd or .bat), selected from the Run File list}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet2|Windows PowerShell|Execute a Windows Powershell script, selected from the Script list}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet2|PowerShell Core|Execute a Windows Powershell Core script, selected from the Script list}} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Timeout|Numeber of seconds before the SIS execution will timeout}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Options / Args|Specifies arguments that can be sent to the pecified command. Input parameters can be used to provide dynamic values}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Input Parameters|Allows for one or more input parameters that can be required or optional, to be specified}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Output Parameters|Allows for one or more output parameters that can be required or optional, to be specified}} | ||
| + | [[File:PackageOperationsFormInputParams.png|350px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Input parameters once created can be referrenced using the following format: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | {param.<input_parameter_name>} | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | <input_parameter_name> should substituted for the relevant parameter name such as {param.host} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using the above format an input parameter can be used as the value for an argument to be sent to the relevant Command Type executable component. The following example shows how a parameter can be used to provide the value to the -n argument used by the '''ping''' command: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | -n 2 "{param.host}" | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Default value and a hint can be set for the Input Parameter. | ||
| + | If the Input Parameter is set as sensitive (struck out eye), then the parameters will be encrypted in transmission as the Credentials are. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{infobox| | ||
| + | * the parameters are ''substituted'', the character escaping needs to be handled by the developer. | ||
| + | * It might be that n/m-dash are substituted with hyphens. | ||
| + | * Fancy quotes might also get added to the substitution list | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is also possible to pass user credentials to the command line. The credentials should be added to the "Extra Credentials" section of the Job definition. To use the credentials use: <pre> | ||
| + | {creds:credential_name.credential_property_name}</pre> eg:<pre> | ||
| + | {creds:credential1.apikey}</pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | It would be well advised to ensure there is clear user documentation as to what Extra Credentials need setting (their exact names as well as their types) when creating these Packages. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Output Parameters can also be configured, the resulting Console Output is then expected to contain text in the following format: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | {{SISJobOutputParameterStart:output_variable_name}}output_data{{SISJobOutputParameterEnd}} | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | The output data can then be used as input for a subsequent Automation call within the Runbook or Business Process (if passed on via the Runbook's Output Parameters). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Script Creation== | ||
| + | ===Supported File Types=== | ||
| + | :{| | ||
| + | |- valign="top" | ||
| + | |style="width:500px"| | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|.bat|Command Prompt Batch process files}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|.sh|Powershell and Powershell Core scripts}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|.js|Javascript}} | ||
| + | |style="width:500px"| | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|.txt|Text format file}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|.json|JavaScript Object Notation file}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|.csv|Comma Seperated Value file}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{infobox| | ||
| + | Some of the supported file types require disabling '''security.fileUploadRestriction.entity.fileAttachments.enable''' or remove the extensions from the '''security.fileUploadRestriction.entity.fileAttachments.types''' list. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | ==Baselining== | ||
| + | In order to keep track of your package developments, you will invariably be working on a Draft. Once you are happy with your draft, '''baseline''' the draft. A new version will become the new published version of the package and ALL existing scheduled jobs using operations from the package will be using this new package. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{infobox|when the Baseline action is clicked, the resulting context will be left in Draft mode. Select a specific version before releasing a home-baked creation to the world (by packaging it). | ||
| + | To recognise in what developing context is, look for '''View Draft''' button and the sub-header on the page which states the version number before '''(Readonly Baseline)''' | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ITOMPackageBaseline.png|ITOM Package Baseline]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Use the down-arrow next to the Baseline button to select the between the different versions of your package - this can be used to compare those versions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ITOMPackageBaselineVersionSelection.png|ITOM Package Baseline Version Selection]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are various actions you can select from on a particular baseline: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Bullet1|Package and Install|this will set the current baseline up as the active baseline for existing items on the '''Job Scheduling'''}} | ||
| + | {{Bullet1|Package and Download|this will result in a .pkg being downloaded which can be shared and uploaded in the '''Installed Packages''' section}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ITOMPackageBaselineOptions.png|ITOM Package Baseline Options]] | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:ITOM]] | [[Category:ITOM]] | ||
Revision as of 15:47, 30 March 2020
| Home > Administration > ITOM > Package Creator | Index |
IntroductionThe Package Creator allows a user, with the necessary programming background and ability, to create Operations within Packages. A Package consists of a single Package Info file and with additional resource files where required. The info file contains all the details regarding operations and all parameters that may be necessary. Although it is possible to manually create a Package, a form-based editor is provided to simplify the process. An interface is also provided to facilitate the uploading and organisation of resources that may be required to facilitate operations. These resources may be scripts, executables or other required files. In addition to uploading scripts, an interface is also provided to allow for various file types to be created via the browser interface. |
|
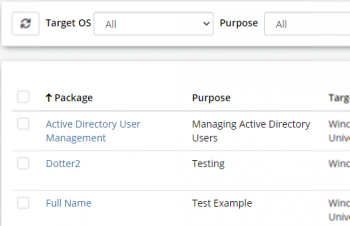
Package Creator List
- Package
- Unique name given to the Package
- Purpose
- Summary of the intended use of the package
- Target OS
- Operating System that the package was designed for execution
- Published
- Late Published version of the packacge
- Created On
- Date that the package was created
- Created By
- The account used to create the package
- Last Updated On
- Date the package was last updated
- Last Updated By
- The account last used to update the package
Toolbar
- Refresh
- Target OS
- All
- Unknown
- Windows 32-bit
- Windows 64-bit
- Windows Universal
- Purpose
- Dynamic list populated from the Purpose field of entriies in the list
- Filter
- Free text filter on Package
-
- Create an IT Automation Package
- Delete
- Delete selected Package(s)
Create a Package
Select the [+] button from the toolbar and when requested, enter a unique Package name. This will display Package Details where the package can be Configured and Updated via the Package Content Frame and Properties Form.
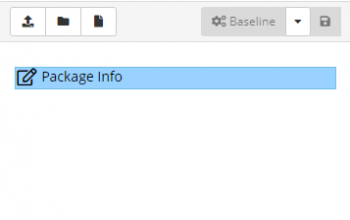
Package Content Toolbar
- Upload
- Uploads files to the current folder
- New Folder
- Creates a new Folder
- New File
- Creates a new file in the current folder
- Baseline
- Creates a new baseline of the current package
- Save
- Saves amended package details
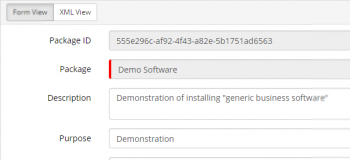
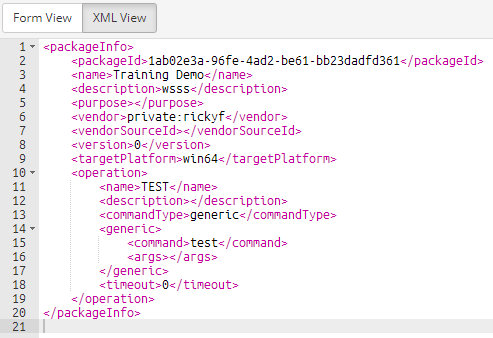
Selecting Package Info file enables the file to be modified via a form or in its native XML format, which is selectable via the toggle buttons.
- Package ID
- A GUID which uniquely identifies the package) will be generated on creation
- Package
- Description
- Description of the packages content
- Purpose
- Summary of the intended use of the package
- Vendor ID
- Defined by the creator of the package (Hornbill packages will set to "private:hornbill")
- Target OS
- Defines Target OS platform that the package is designed
- Windows 32-bit
- Windows 64-bit
- Windows Universal
- Package can be invoked on either Windows 32 or 64-bit
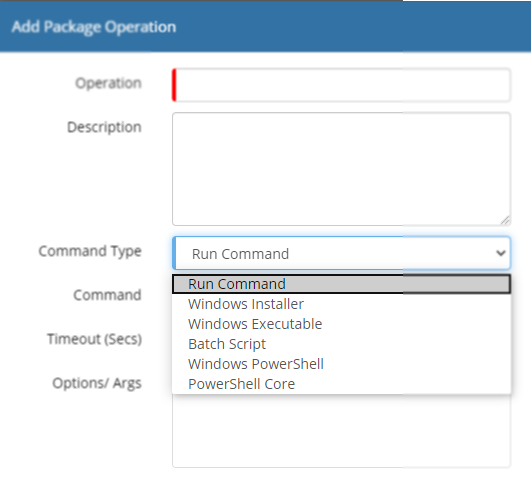
Package Operations
Operations various actions to be configured, which execute a single command, executable, script or installer package. An Operation is created by clicking on the Add Operation button within the Form View.
- Operation
- Mandatory Name used to select the package when creating a Job
- Description
- Describes the functionality provided by the operation
- Command Type
- Provides a list of supported command types
- Run Command
- Executes a standalone command
- Windows Installer
- Executes an uploaded Windows Installer(.msi) package, with one of four actions are available
- Install Software
- Installs the .msi package
- Run Program
- Executes the Installed program
- Uninstall Software
- Uninstall an .msi package
- Update Software
- Update an Installed .msi package
- Windows Executable
- Executes a windows executable, selected from the Run File list
- Batch Script
- Excutes a Windows batch script (.cmd or .bat), selected from the Run File list
- Windows PowerShell
- Execute a Windows Powershell script, selected from the Script list
- PowerShell Core
- Execute a Windows Powershell Core script, selected from the Script list
- Timeout
- Numeber of seconds before the SIS execution will timeout
- Options / Args
- Specifies arguments that can be sent to the pecified command. Input parameters can be used to provide dynamic values
- Input Parameters
- Allows for one or more input parameters that can be required or optional, to be specified
- Output Parameters
- Allows for one or more output parameters that can be required or optional, to be specified
Input parameters once created can be referrenced using the following format:
{param.<input_parameter_name>}
<input_parameter_name> should substituted for the relevant parameter name such as {param.host}
Using the above format an input parameter can be used as the value for an argument to be sent to the relevant Command Type executable component. The following example shows how a parameter can be used to provide the value to the -n argument used by the ping command:
-n 2 "{param.host}"
Default value and a hint can be set for the Input Parameter. If the Input Parameter is set as sensitive (struck out eye), then the parameters will be encrypted in transmission as the Credentials are.
- the parameters are substituted, the character escaping needs to be handled by the developer.
- It might be that n/m-dash are substituted with hyphens.
- Fancy quotes might also get added to the substitution list
It is also possible to pass user credentials to the command line. The credentials should be added to the "Extra Credentials" section of the Job definition. To use the credentials use:
{creds:credential_name.credential_property_name}eg:
{creds:credential1.apikey}
It would be well advised to ensure there is clear user documentation as to what Extra Credentials need setting (their exact names as well as their types) when creating these Packages.
Output Parameters can also be configured, the resulting Console Output is then expected to contain text in the following format:
{{SISJobOutputParameterStart:output_variable_name}}output_data{{SISJobOutputParameterEnd}}
The output data can then be used as input for a subsequent Automation call within the Runbook or Business Process (if passed on via the Runbook's Output Parameters).
Script Creation
Supported File Types
- .bat
- Command Prompt Batch process files
- .sh
- Powershell and Powershell Core scripts
- .js
- Javascript
- .txt
- Text format file
- .json
- JavaScript Object Notation file
- .csv
- Comma Seperated Value file
Some of the supported file types require disabling security.fileUploadRestriction.entity.fileAttachments.enable or remove the extensions from the security.fileUploadRestriction.entity.fileAttachments.types list.
Baselining
In order to keep track of your package developments, you will invariably be working on a Draft. Once you are happy with your draft, baseline the draft. A new version will become the new published version of the package and ALL existing scheduled jobs using operations from the package will be using this new package.
- when the Baseline action is clicked, the resulting context will be left in Draft mode. Select a specific version before releasing a home-baked creation to the world (by packaging it).
To recognise in what developing context is, look for View Draft button and the sub-header on the page which states the version number before (Readonly Baseline)
Use the down-arrow next to the Baseline button to select the between the different versions of your package - this can be used to compare those versions.
ITOM Package Baseline Version Selection
There are various actions you can select from on a particular baseline:
- Package and Install
- this will set the current baseline up as the active baseline for existing items on the Job Scheduling
- Package and Download
- this will result in a .pkg being downloaded which can be shared and uploaded in the Installed Packages section