Application and Interface Security
Application and Interface Security
All software is written/maintained in-house using a combination of C++ and JavaScript server-side, and HTML/CSS/JS for frontend development
All applications and all programming interfaces are designed with the various NIST known patterns for secure programming and tested against the OWASP top 10. Both Automated and manual tests are used to detect security defects (amongst others) in code prior to production. Inputs are sanity checked and integrity routines in place against applications and databases, and development frameworks deployed to make it impossible to generate common vulnerabilities such as SQL injection issues, to prevent manual or systematic processing errors, corruption of data, or misuse.
Hornbill's architecture, design and development processes all incorporate in-depth consideration of the OWASP Top 10 Application Security Risks. Hornbill seeks to ensure its staff and processes are informed about the consequences of the most common and most important web application security weaknesses.
Hornbills' data security model is the principle of least privilege and based on the idea of minimum rights for each individual to perform any given task. All-access is checked\granted by the server as required from the list of rights associated with the account at the time of use and can be elevated to perform the action if the user is permitted. If multiple roles\rights are associated with the user that would permit an action then the lowest is used
The principle of least privilege means.
- Better system stability. When code is limited in the scope of changes it can make to a system, it is easier to test its possible actions and interactions with other APIs.
- Better system security. When code is limited in the system-wide actions it may perform, vulnerabilities in one application cannot be used to exploit the integrity of another application.
- Ease of deployment. In general, the fewer privileges an application requires the easier it is to deploy within a larger environment.
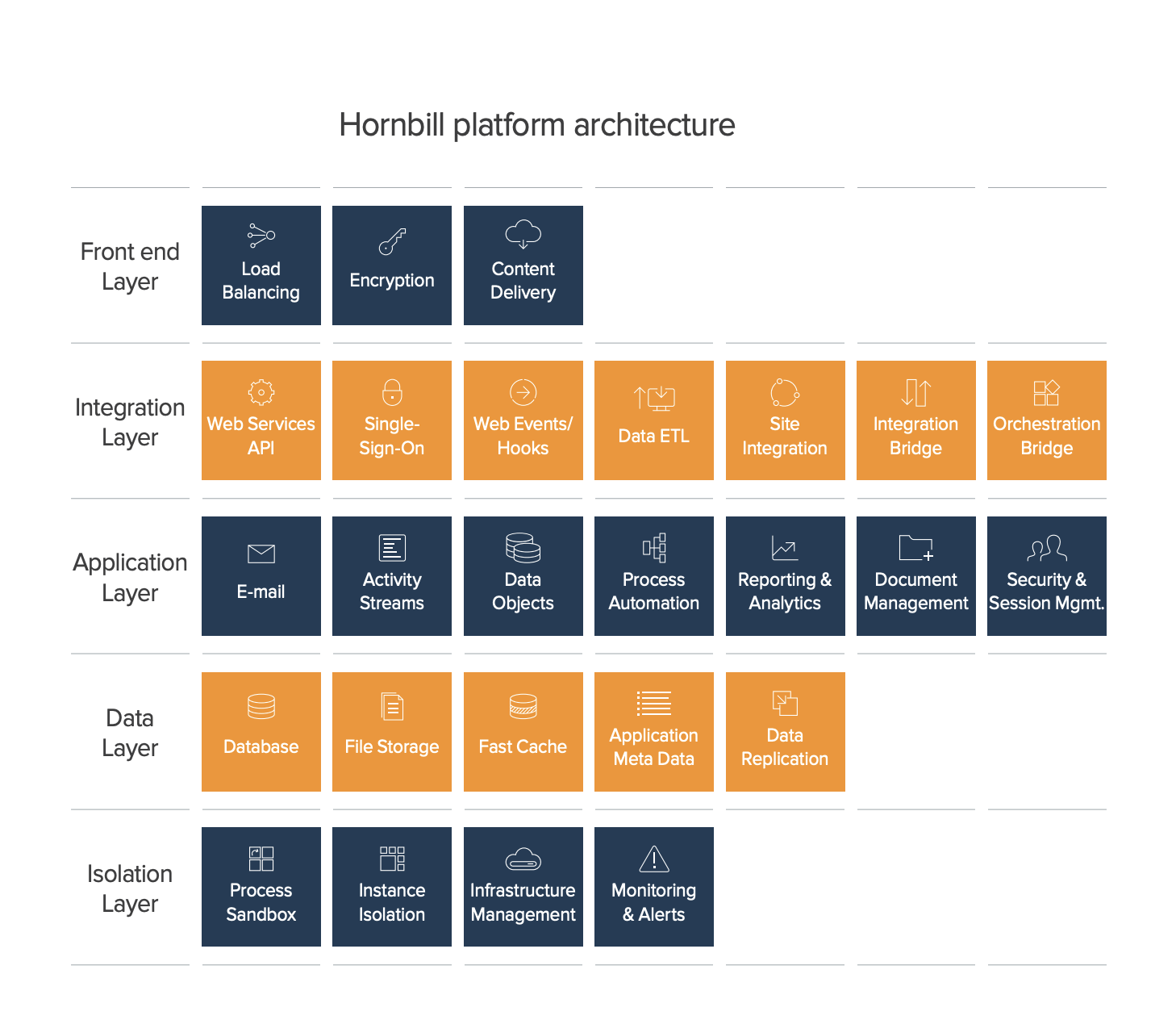
The below is a high level application diagram.